
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Science, Changchun University of Science and Technology, Changchun 130022, China
2 State Key Laboratory for Mesoscopic Physics and Collaborative Innovation Center of Quantum Matter, Department of Physics, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
It is highly desirable to flexibly and actively manipulate the dephasing time of a plasmon in many potential applications; however, this remains a challenge. In this work, by using femtosecond time-resolved photoemission electron microscopy, we experimentally demonstrated that the Fano resonance mode in the asymmetric nanorod dimer can greatly extend the dephasing time of a femtosecond plasmon, whereas the non-Fano resonance results in a smaller dephasing time due to the large radiative damping, and flexible manipulation of the dephasing time can be realized by adjusting one of the nanorods in the Fano asymmetric dimer. Interestingly, it was found that plasmon resonance wavelengths both appeared red-shifted as the length of the upper or lower nanorods increased individually, but the dephasing time varied. Furthermore, it also indicated that the dephasing time can be prolonged with a smaller ascending rate by increasing the length of both the nanorods simultaneously while keeping the dimer asymmetry. Meanwhile, the roles of radiative and nonradiative damping in dephasing time are unveiled in the process of nanorod length variation. These results are well supported by numerical simulations and calculations.
Photonics Research
2022, 10(10): 2267
开展结构Sn靶激光等离子体极紫外光辐射特性研究,对波长为1064 nm的脉冲激光等离子体产生的极紫外光谱进行研究。实验结果表明,当激光能量为500 mJ,结构靶凹槽深度为100 μm、宽度为300 μm时,结构靶凹槽产生13.5 nm(2%带宽)带内光辐射积分强度的增强倍率约为平面靶的1.57倍。同时发现,凹槽对激光等离子体膨胀具有抑制作用,导致不同凹槽宽度产生最佳增强倍率所对应的激光能量不同。研究聚焦光斑尺寸对结构靶产生极紫外光辐射的影响。实验结果表明,当聚焦光斑直径与凹槽宽度接近时,凹槽的13.5 nm(2%带宽)带内光辐射积分强度的增强倍率最高。此项研究对提高极紫外光辐射强度及转换效率具有重要意义。
光谱学 极紫外辐射 激光等离子体 结构靶 光刻光源 中国激光
2021, 48(16): 1601005

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Physics, Changchun University of Science and Technology, Changchun 130022, China
2 e-mail: songxiaowei@cust.edu.cn
3 e-mail: linjingquan@cust.edu.cn
Ultrafast spatiotemporal control of a surface plasmon polariton (SPP) launch direction is a prerequisite for ultrafast information processing in plasmonic nanocircuit components such as ultrafast on–off of plasmonic switching and information recording. Here we realize for the first time, to the best of our knowledge, ultrafast spatiotemporal control of the preferential launch direction of an SPP at the nano-femtosecond scale via a plasmonic nano directional coupler. The spatiotemporal switching of the SPP field was revealed using time-resolved photoemission electron microscopy (TR-PEEM). Experimental results show that the extinction ratio of the SPP directional coupler can be substantially optimized by properly selecting the amplitude and time delay of the two incident light pulses in the experiment. More importantly, we demonstrate a solution for the launch direction of the SPP field, switched in a plasmonic nano directional coupler on the femtosecond timescale, by adjusting the instantaneous polarization state of the excitation light. The TR-PEEM images are supported by finite-difference time-domain (FDTD) simulations. We believe the results of this study can be used to develop high-speed, miniaturized signal processing systems.
Photonics Research
2021, 9(4): 04000514
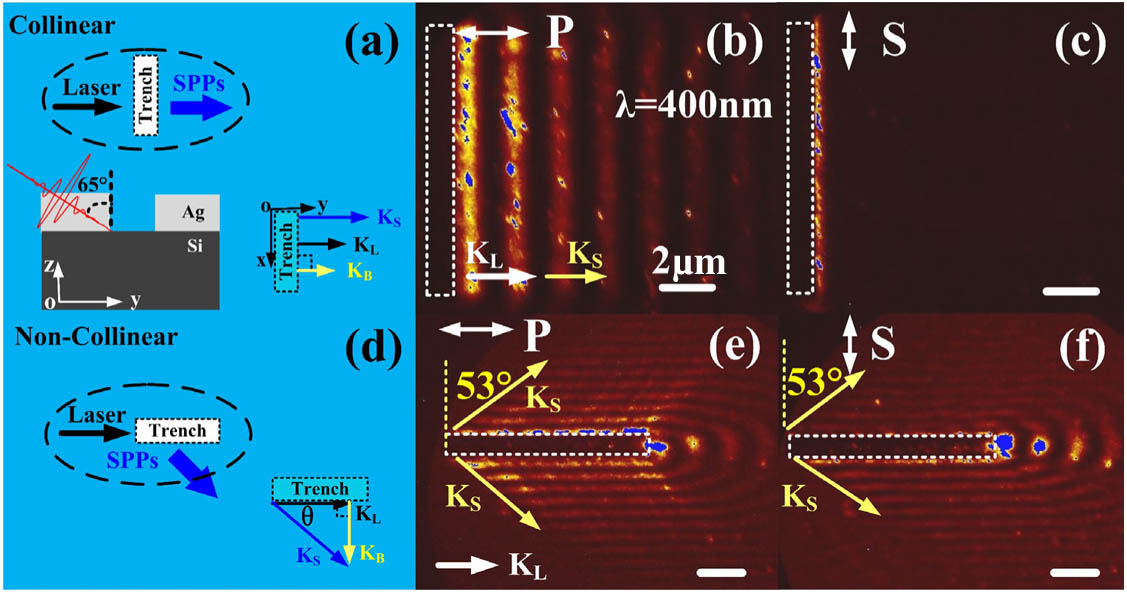
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Physics, Changchun University of Science and Technology, Changchun 130022, China
2 e-mail: songxiaowei@cust.edu.cn
The comprehensive capture of near-field spatiotemporal information of surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs) is a prerequisite for revealing their physical nature. In this study, we first performed an independent, spatiotemporal imaging of the out-of-plane and in-plane components of SPP near-fields in a femtosecond light-excited trench using an obliquely incident time-resolved photoemission electron microscopy (TR-PEEM). We did the capture by imaging of the interference patterns induced by a superposition of the - or -polarized probe light, with the out-plane or in-plane components of SPP near-fields, under the noncollinear excitation mode. The method may be used to reconstruct a 3D SPP spatiotemporal field. Moreover, we demonstrated that the fringe shift of the interference patterns between the captured in-plane and out-of-plane components of the SPP field in PEEM images corresponds to the 1/4 fringe period, which is attributed to out of phase of the out-of-plane and in-plane near-field components of SPP. The resulting TR-PEEM images are supported by a classical wave mode and FDTD simulations. Essentially, the measured phase difference between the in-plane and out-of-plane components of the SPP indicated a rotating field component in the propagation plane, i.e., that the SPP exhibits an elliptically polarized electric field in the propagation plane. The experimental results presented herein provide direct evidence of SPP having the inherent attributes of transverse spin angular momentum.
Photonics Research
2020, 8(6): 06001042
Author Affiliations
Abstract
School of Science, Changchun University of Science and Technology, Changchun 130022, China
Metals in nature exhibit a mediocre wettability and a high optical reflectance from the visible region to the infrared. This Letter reports that, by formation of nano- and microscale structures via a simple raster scanning of a focused femtosecond laser pulse without any further treatment, structured aluminum and nickel surfaces exhibit combined features of superhydrophobicity with a contact angle of 155.5°, and a high optical absorption with a reflectivity of several percent over a broad spectral range (0.2–2.5 μm). Thus, a multifunctional structured metal surface that integrates superhydrophobicity and a high broadband absorptivity has been easily realized by one-step femtosecond laser processing.
140.3390 Laser materials processing 160.4236 Nanomaterials 240.6700 Surfaces Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(6): 061402
1 长春理工大学理学院, 吉林 长春 130022
2 包头师范学院物理科学与技术学院, 内蒙古 包头 014030
对波长355 nm,脉宽5 ns的激光脉冲烧蚀空气中光学玻璃产生的等离子体发射光谱进行了时间和空间分辨研究。结果表明,在等离子体羽膨胀初期(小于200 ns时间范围内),等离子体发射光谱主要由连续光谱构成。此后,连续光谱强度逐渐减弱,线状光谱开始占主导地位。实验表明,由于存在等离子体屏蔽效应,脉冲能量大于35 mJ后,光谱线强度开始减弱。由时间分辨发射光谱发现,在等离子体羽膨胀过程中等离子体辐射波长(以Si I 390.6 nm为例)存在红移现象,波长红移量随时间演化呈二次指数衰减。
光谱学 脉冲激光烧蚀 等离子体发射光谱 谱线强度 光谱红移
1 长春理工大学 理学院,吉林 长春 130022
2 包头师范学院 物理科学与技术学院,内蒙古 包头 014030
利用YAG脉冲激光烧蚀(PLA)空气环境中的Fe靶,观测激光诱导等离子体发射光谱。采用不同脉冲能量,对380.0-420.0 nm的等离子体发射光谱进行了时间、空间分辨研究。在局部热力学平衡条件下,根据所测谱线的相对强度,利用Saha方程得到等离子体电子温度约为104 K。根据测得谱线的半峰全宽(FWHM),推得等离子体电子密度约为1017 cm-3。给出了靶面附近等离子体电子温度、电子密度的时间及空间演化规律。
激光技术 激光烧蚀 等离子体发射光谱 电子温度 电子密度
北京工业大学 北京光电子技术实验室, 北京 100124
共振腔发光二极管(RCLED)是一种新型发光二极管(LED) 结构, 同时具备了传统LED和垂直腔面激光器(VCSEL)两者的优点, 具有良好的应用价值和广阔的市场前景。介绍了RCLED的基本原理和结构, 以及器件结构的设计要点, 指出发射波长650 nm 的RCLED在塑料光纤(POF)通信领域的应用优势, 可以作为民用数据通讯系统用光发射器件的首选。对近年来RCLED尤其是红光波长范围的RCLED发展情况进行了概述, 同时指出我国在这一领域的研究现状。
共振腔发光二极管 微腔发光二极管 红光 塑料光纤 激光与光电子学进展
2008, 45(12): 25





